| Rhythm Centre :: Rhythm and Healing :: Research and Studies |
| "Composite effects of group drumming music therapy on modulation of neuroendocrine-immune parameters in normal subjects." - Page 7 |
...BACK
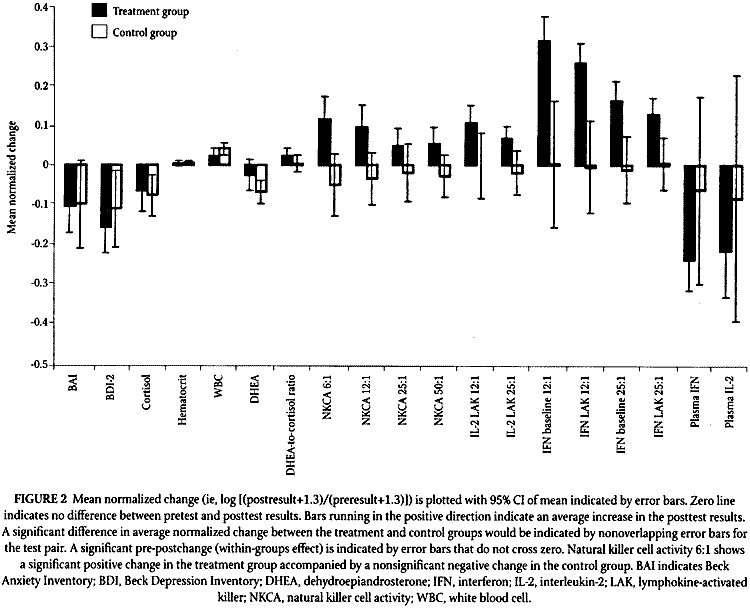 |
The finding of elevated DHEA-to-cortisol ratios in experimental subjects in the present study suggests a shift in adrenal steroids in an immunoenhancing direction. This shift could potentially enhance cell-mediated (TH1) immune reactivity and is consistent with enhanced LAK cell activity observed at the end of the drumming session in the experimental group. It is unlikely that the DHEA-to-cortisol ratio was elevated solely because of the exercise component of the drumming. Milani and coEeagues/44 showed that exercise training alone has no significant impact on DHEA sulfate; however, behavioral therapy in combination with exercise training did elevate DHEA sulfate. In addition, qigong training in humans did not elevate DHEA sulfate or change cortisol levels./45 Furthermore, data from preliminary studies failed to demonstrate elevations of DHEA-to-cortisol ratios associated with other drumming interventions, one of which included higher levels of exercise than ultimately used in the treatment group.
Based
on the failure of some of the researchers' preliminary drumming trials
to modulate neuroimmune parameters, the unique combination of components
in the composite drumming sessions, including the music therapist's approach,
exercise, music, and guided imagery, may have exerted a collective effect
on immune modulation and adrenal steroids to elevate the DHEA-to-cortisol
ratio.
Van der Berghe et al/43
have shown that DHEA and cortisol secretions are under separate central
nervous system regulatory control, thereby providing ample opportunity
for a complex activity such as drumming to exert emotional and cognitive
influences on this central regulatory circuitry. In one preliminary study
group, subjects listened to drum music generated by an experimental group.
Other groups drummed without introductory warm-up activities or drumming
guided imagery according to the present protocol. Another performed intense
drumming without these associated activities. No significant results in
any measures other than cortisol reduction were found from subjects who
participated in these drumming groups. According to the present protocol,
then, drumming appears to be a complex composite activity with key individual
components that, in unique combination, appear to be responsible for the
measured neuroendocrine and neuroimmunological changes.
NK cells are large granular lymphocytes,
major components of the innate immune system, with mixed lymphocyte/mono-cyte/granulocyte
surface markers. MORE..